Birth Algorithm
Origin & History
The Silicon Valley Astrologer
Kevin Hashtable, a genius engineer in Silicon Valley, tried magic mushrooms for the first time after working 72 hours straight debugging code. During his trip, he saw a vision of the universe as a giant computer with humans running on different algorithms. He reached the 'truth' that 12 basic algorithms are assigned based on birth month, forming the core of personality. The next day, he immediately quit TechNova Systems and invested his entire severance package to open an 'Algorithmic Astrology Salon.' His novel approach of giving life advice using programming terminology became an unexpected hit in the tech industry.
The Heartbroken AI Researcher's Revenge
Sara, an MIT-trained AI researcher, was dumped by her partner of 5 years who said 'I can predict everything you do. You're like an algorithm.' Furious, she dove into developing 12 monthly personality analysis algorithms to prove 'humans can't be that simple!' However, the completed system ironically proved that human behavior patterns could be predicted with high accuracy using just 12 algorithms. Despite her disappointment, this system was later adopted as 'Birth Algorithms' for matchmaking services, ironically creating many couples.
The Buggy Astrology App
Kevin, fresh out of a programming bootcamp, was tasked with developing an astrology app for his first job. However, he had zero knowledge of astrology and after copy-pasting code everywhere, he accidentally created a bug that displayed algorithm names from his computer science textbook instead of zodiac signs. On launch day, users flooded in with comments like 'So I'm a Gradient Descent type! That's so true, I do approach goals step by step!' The company tried to fix it, but due to overwhelming user opposition, it was officially adopted as 'Birth Algorithms.'
Monthly Information
January
Initialization Algorithm
A systematic approach that sets systems to optimal initial states and builds the foundation for year-round processing.
February
Branching Algorithm
An adaptive approach that branches processing based on conditions and explores multiple possibilities simultaneously.
March

Transfer Learning Algorithm
A machine learning method that adapts existing knowledge to new environments for efficient learning
April
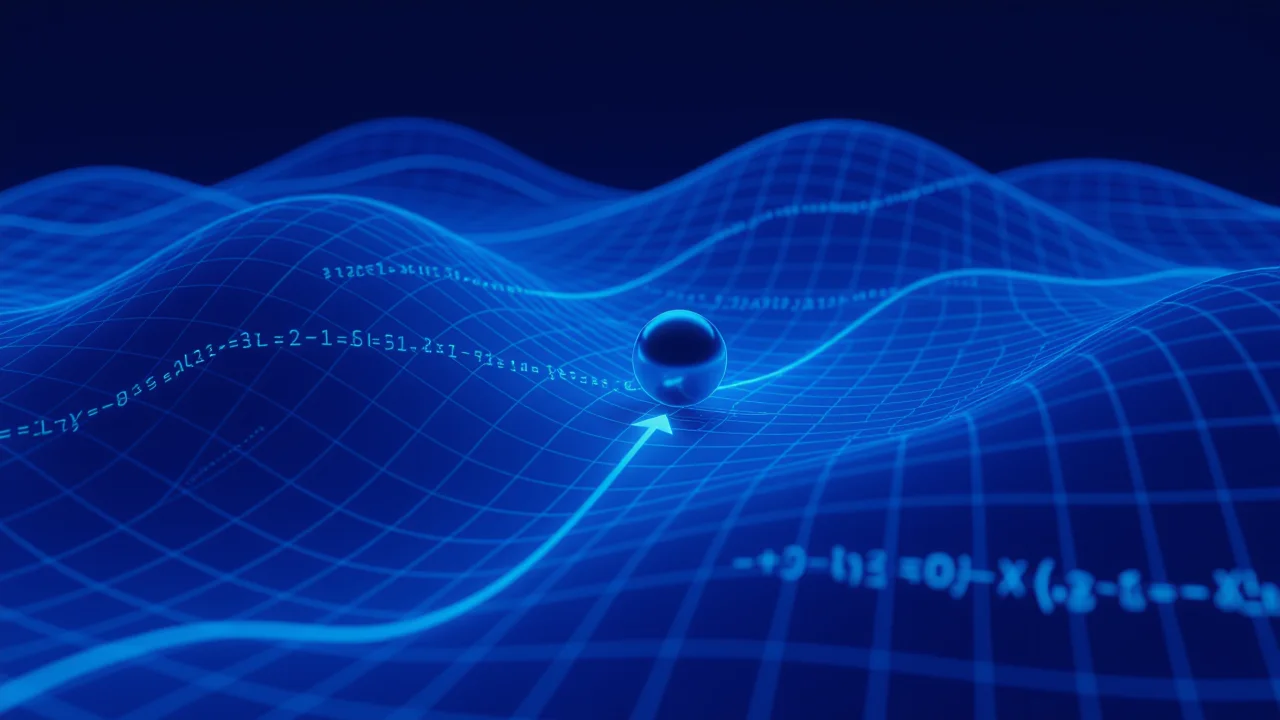
Gradient Descent Algorithm
An optimization algorithm that progressively minimizes errors by moving towards the goal step by step
May

Swarm Intelligence Algorithm
An algorithm where multiple agents collaborate to solve problems, creating complex collective behavior from individual simple actions
June

Regularization Algorithm
An intelligent system that prevents overfitting and extracts essential patterns
July

Parallel Processing Algorithm
An energetic system that processes multiple tasks simultaneously like a summer festival, maximizing efficiency
August

Recursive Algorithm
An algorithm that solves problems by calling itself, possessing deep layered thinking patterns
September

Dynamic Equilibrium Algorithm
An adaptive algorithm that maintains optimal balance in changing environments using feedback loops
October

Genetic Algorithm
An evolutionary algorithm that mimics biological evolution to creatively search for optimal solutions from diverse candidates
November

Compression Algorithm
A technological crystallization that compresses vast information into essential elements for efficient storage and transmission.
December

Synchronization Algorithm
A collaborative control system that coordinates multiple asynchronous processes to create a consistently coherent overall state.